What is Proof of Work?5 min read
Reading Time: 4 minutesProof of Work is the consensus algorithm that powers the Bitcoin network and prevents double-spending. A double spend happens when the same funds are spent twice, and if this were to happen it would essentially break the Bitcoin network. To better understand how Proof of Work maintains the decentralized integrity of the Bitcoin network, you need to understand the following key concepts:
- What is Proof of Work
- Byzantine General Problem
- How it applies to Bitcoin
- Why do we need Proof of Work
What stops someone from modifying and altering a Bitcoin transaction? In simple terms Proof of work means that work needs to be done to earn the reward. Proof of Work is a consensus mechanism that ensures that transactions are accurate and not altered. In Bitcoin, to validate transactions, miners need to solve a complex mathematical puzzle. To solve the puzzle, miners spend a significant amount of computational power and electricity, and for it, they are rewarded with newly minted bitcoin and fees. PoW requires that a substantial amount of electricity is spent for mining a block which is expensive and requires specialized computers called ASIC. Proof of Work incentivizes miners not to cheat and instead makes it profitable to act honestly.
What is Proof of Work
A proof of work is achieved when miners solve a block to “prove” that they have put in the computational resources by solving a cryptographic puzzle to verify transactions and add a new block of transactions to the blockchain.
In Bitcoin, all transactions must be validated by miners. To validate blocks of transactions miners need to find the solution to the proof of work. In order to do so, miners hash the block header using the nonce (number used only once). This is the only piece in the block that can be changed. The nonce allows miners to vary it and iterate through it to create a hash. The Bitcoin protocol will set a target for miners to find a certain hash under a certain range called the target. Any hash that is above this set target will be rejected, and the hash will not be used to create a new block. However if a miner finds a hash inside the algorithm’s set target, then the hash can be used to produce a new block. This problem is called the proof of work problem as it requires the miner to have done some work in finding out the solution to the problem and hence the mined block must be valid.
After the miner finds a hash under the target, the Proof of Work consensus algorithm verifies the hash with other nodes on the network. Nodes will independently validate each block and ensure that the block is valid before it propagates it to its peers. If accepted by all the nodes, the transaction is added to the blockchain by the miner. In return for the miner’s contribution, they receive the ‘block reward’ and the fees as compensation. This is important as acting dishonestly will mean that the miners will lose their reward but also have to incur the cost to find the Proof of Work solution. The purpose of a consensus mechanism is to bring all the nodes in agreement and create trust in an environment where the nodes don’t trust each other.
Byzantine Generals Problem
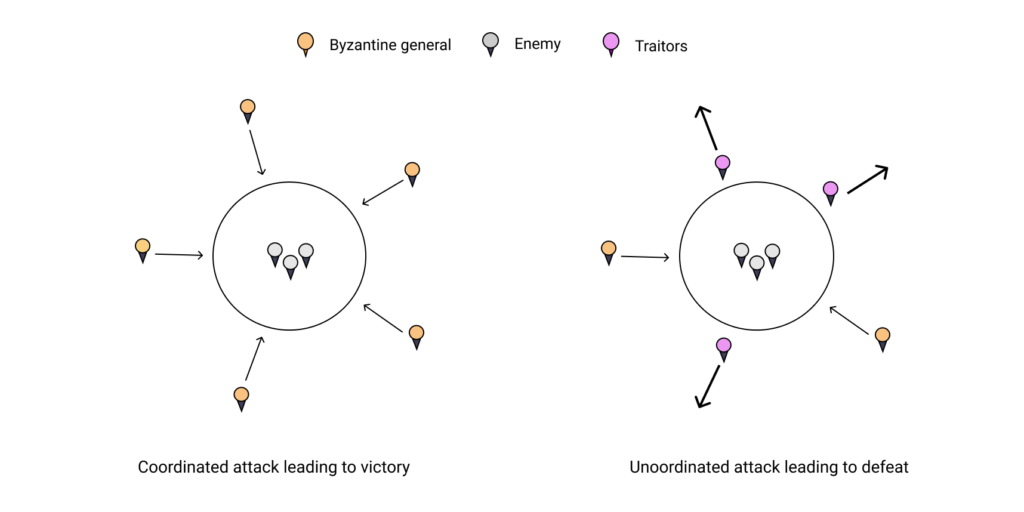
Let’s imagine a scenario where generals are attacking a common enemy. The scenario assumes that each general has its army and that each general is situated in different locations around the common enemy that they intend to attack. There are traitors and we do not know who they are in this scenario. The generals need to decide whether to attack or retreat. The generals can only win if the majority of the generals come into agreement. However, if they have chaos and don’t reach a consensus, they will be destroyed by the enemy. The generals can only communicate by passing messages via messengers between them. The messengers may lie or get corrupted on the way. How can the generals come to a consensus despite their being traitors?
How does this problem apply to Bitcoin?
Decentralized systems like Bitcoin encounter a similar problem as nodes do no not trust each other. Bitcoin is the first solution to this problem. It allows peers to reach a consensus without any central entity. Bitcoin achieves this by using Proof of Work. Proof of Work solves this problem by making it extremely difficult to alter the messages.
The Bitcoin blockchain is a distributed ledger that functions like the Byzantine generals’ distributed attack. Broadcasting blocks to the network is like the attack messages of the generals. Much like the generals, how can the network trust the other members and ensure that the messages are valid.
Before broadcasting their message to the network, a miner must solve a complex mathematical problem called the proof of work puzzle. Blocks are considered valid by all network members only if they contain a valid Proof-of-Work in the form of a valid hash. This allows decentralized nodes to agree on a specific block to be added to the chain. The proof of work does not prove that the block is valid but instead it shows that energy was expended to produce it. The work required to produce a block discourages miners from building invalid or empty blocks, as it would be rejected by all the other nodes. Miners are additionally incentivized to create valid blocks because of the block reward by which they receive newly minted bitcoin and the transaction fees.
Why do we need proof of Work?
Suppose a miner decides to solve for and broadcast an invalid block (one with false transactions). In that case, the network will reject it, and the miner would have wasted their electricity and computational power on solving for the hash that would have allowed for the block to be added to the blockchain. This would mean that the miner has wasted computational power. Thus, the system incentivizes miners to play by the rules and work on valid blocks. If it didn’t require a lot of computational power and energy to mine, there would be no incentive for miners to mine honestly. The network will automatically reject any block that includes an invalid transaction. It’s expensive for miners even to attempt to cheat.

