Growth of the Bitcoin Lightning Network5 min read
Reading Time: 4 minutesThe Bitcoin Lightning Network has seen significant growth and adoption since the beta launch in March 2018. LN continues to mature and harden at pace, notably as relates to:
- network liquidity and resilience
- protocol and capability development
- user experience
- new Lightning-focused startups
- Consumer & Merchant adoption
The Passing of the Lightning Torch
An early galvanizing event was the passing of the Lightning Network Torch, a Lightning Network payment chain facilitated by bitcoin users using Twitter in the first quarter of 2019. Started by Twitter user Hodlonaut, the Lightning Torch went viral, raising awareness of and generating excitement for the protocol. A few celebrities and influencers, including Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey, received the torch before it reached its final destination, the Bitcoin for Venezuela Initiative.
Bitcoin Lightning Network Wallets
Consumer adoption of Bitcoin payments depends in large part on a simple, intuitive mobile wallet user experience. 2018 and 2019 were banner years for new Lightning Network wallets, including Wallet of Satoshi, Breez, Blue Wallet, and Eclair.
Breez in particular was the first non-custodial wallet to introduce a Neutrino-based client, incorporating a light client – or LND – to allow access to a scaled-down version of the Bitcoin Blockchain, while minimizing the amount of CPU and data required to send and receive payments via mobile device.
Bitcoin to Lightning On-Ramps
Transactions between on-chain Bitcoin addresses and off-chain LN addresses are not directly compatible. Introduced in late 2018, Submarine Swaps eliminate the historically complicated task of getting Bitcoin into the Lightning Network by using a trustless intermediary to transfer tokens between blockchains. This allows off-chain LN channels to be refilled directly through an on-chain transfer from the Bitcoin blockchain.
Fiat to Lighting On-Ramps
In late 2019, developers from Lightning-focused companies like Zap, Sparkswap, and Escher brought simplified fiat to Lightning on-ramps to market. With Olympus from Zap, for example, users can purchase BTC with fiat and begin sending and receiving Lightning Network payments quickly and conveniently.
Bitcoin Exchanges using Lightning
Bitfinex was the first major Bitcoin exchange to add support for the Lightning Network in late 2019. Several other Bitcoin exchanges now also use the Lightning Network protocol: HodlHodl, Buda, and River Financial. By adding support for LN on their platforms, exchanges provide the benefits of instant deposits/withdrawals and super low fees to their users.
Growth of the Bitcoin Lightning Network Public Channels
The Lightning Network supports two types of channels: Public and Private.
Private channels are not broadcast to the Lightning Network and are only known and used by the two involved nodes. It is possible for entire nodes not to be known to the network and in fact, currently, all mobile wallet channels are private. The benefits of Private channels are end-user privacy and more efficient transaction routing.
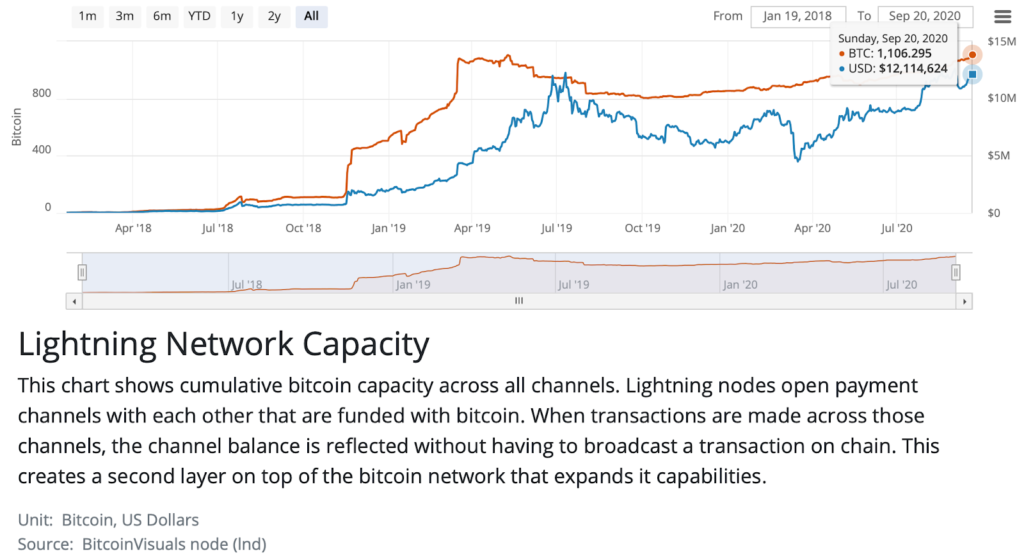
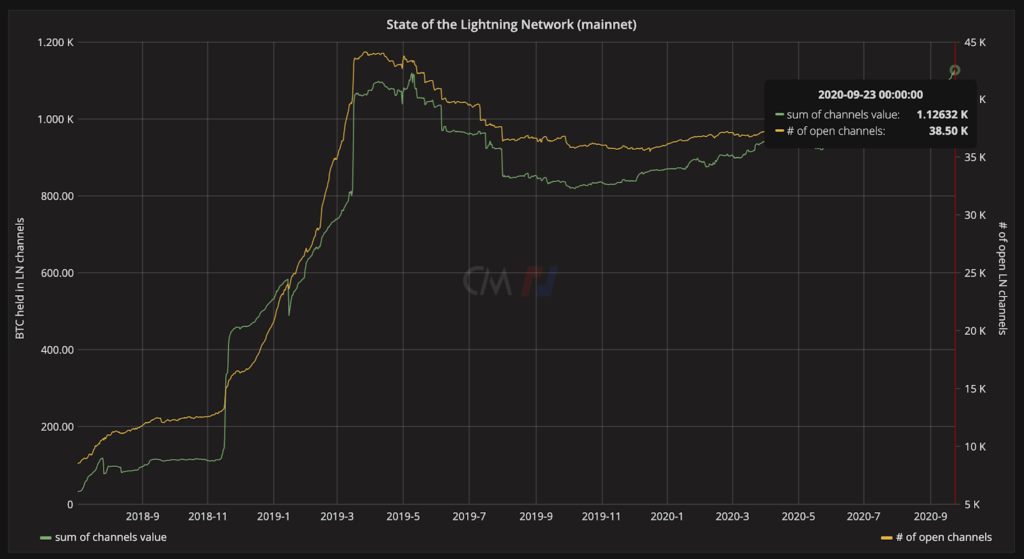
The growth of Public channels can be tracked because their activity is known by the network. According to Bitmex Research, the estimated proportion of Public channels on the network is 72%, and Private channels 28%. The number of unique payment channels is rising, with more nodes joining the network. Since January 2019, the number of public channels has risen from 21,000 to 38,500 and the amount of BTC in those channels has risen from 540 to 1,126 BTC.
Liquidity
Two Lightning Network improvements complement each other to increase utility and improve the experience of sending and receiving payments.
Multi-Path Bitcoin Payments
Multi-path payments enable the ability to break a single payment into smaller pieces that can use multiple channels to settle. The probability of successfully sending larger Bitcoin payments increases significantly because the maximum transfer size is no longer limited by the balance on a given channel. In addition, multi-path payments further decentralize the Lightning Network and make it more censor-resistant.
Large Volume and Higher Value Payments with Wumbo
With limits on channel sizes, Lightning Network node operators have historically been constrained in the amount of Bitcoin they can store on a Lightning Network channel. Wumbo refers to the removal of these channel size limits.
Support for Wumbo channels allows users to deposit and withdraw more money into Lightning Network channels, as well as send larger transactions. As a leader in Lightning Network Bitcoin payments for merchants, OpenNode fully supports Wumbo and has set a limit of 5 BTC Lightning Network transactions on the platform.
What Else & What’s Next?
Continuing to identify & implement improvements
Even though the Lightning Network is fully operational today, there are still some limitations and vulnerabilities that need to be addressed for the Lightning Network to scale the entire Bitcoin ecosystem. Teams like Lightning Labs, ACINQ, and Blockstream are building on Lightning Network infrastructure every day and continuing to advance the network but with payment technology, perfection cannot be rushed.
New applications and use cases
As the growth of the Lightning Network continues, expect to see new businesses and applications accepting Bitcoin Lightning Network payments. The Lightning Network provides the perfect payment infrastructure with instant low-cost transactions so it’s only a matter of time till more businesses start using it. Bitcoin transactions on the Lightning network will be the future of microtransactions on the internet.
At OpenNode, we are strong believers in Bitcoin and are committed to the adoption of the Lightning Network by merchants and payers around the world. We support the Lightning Network as the scaling solution for Bitcoin and will continue to build our payment infrastructure on the protocol’s foundations.
References

